Jupyter Introduction
So launch the Jupiter notebook from your machine
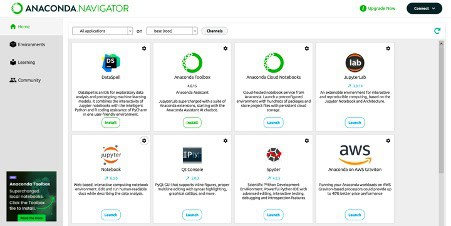
Then Create a new python file by clicking on “New” option and the click on “Python 3”

Then new file will get created and That’s it…you can start your coding now…Good Luck!

Below are the important points which we need to learn to use Jupyter notebook :
1) Model of cell : There are two type of mode as below,
i) In Command Mode
- is the mode where you can perform actions like moving, deleting, inserting, and executing cells.
- The current cell has a blue border when you’re in Command Mode.
ii) In Edit Mode
- is the mode where you can edit the content inside a cell, whether it’s code or markdown.
- The current cell has a green border when you’re in Edit Mode.
- you’ll need to press Esc first to switch to Command Mode
2) Types of cell : In Jupyter Notebooks, there are different cell types that you can use to organize your content. Here’s a quick summary of the different types of cells and how they are used:
i) Code Cell
- Code cells allow you to write and execute Python code (or other supported languages like R, Julia, etc.).
- These cells are executed when you run them (Shift + Enter), and you can use them for computations, data manipulations, visualizations, etc.
# This is a code cell
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3])
arr ** 2
ii) Markdown Cell
- Markdown cells are used for adding text, explanations, and documentation.
- You can format the text using Markdown syntax (headings, lists, bold, italics, etc.) and even include LaTeX for mathematical expressions.
# This is a code cell
Bold text
italic text
iii) Raw NBConvert Cell
- Raw NBConvert cells allow you to add raw content that will be passed unchanged when the notebook is converted (e.g., to HTML, PDF, etc.).
- This can be useful if you’re preparing the notebook for export and need to insert content that should not be processed by the notebook.
iv) Heading in Markdown Cells
- Headings are created in Markdown by using the # symbols. The number of # symbols indicates the level of the heading (from # for the largest heading to ###### for the smallest).
# This is a code cell
Heading 2
Heading 3
Heading 4
Heading 5
Heading6
Common Shortcuts:
- `Shift + Enter`: Run the current cell and move to the next one.
- `Ctrl + Enter`: Run the current cell but stay in the same cell.
- `Esc`: Enter command mode (blue border around the cell).
- `Enter`: Enter edit mode (green border around the cell).
